The Rise of the Industrial Metaverse: A Weak Signal with Potential to Disrupt Manufacturing and Beyond
Emerging technologies are blending in novel ways to reshape how industries operate and innovate. One weak signal gaining momentum is the industrial metaverse—an integrated virtual-physical environment where manufacturing processes, human-machine collaboration, and operational management converge using augmented reality (AR), digital twins, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms. While still nascent, this trend could transform not only manufacturing but also supply chains, healthcare, logistics, and retail sectors, paving the way for new efficiency paradigms and business models over the next decade.
What’s Changing?
The industrial metaverse combines digital twin technology—virtual replicas of physical assets and processes—with immersive AR interfaces and AI-powered analytics to create interactive, real-time operational environments. This development is accelerating as organizations push for smarter, greener, and more resilient industrial ecosystems.
Several connected developments illustrate this trajectory. By 2026, industry leaders anticipate the convergence of AI, IoT, blockchain, and digital twins to facilitate unprecedented operational insight and flexibility (Stat Times, 2025). Digital twins, initially confined to simulation and predictive maintenance, are expected to evolve into interactive platforms where human operators can collaborate with machines in virtual spaces overlaying real-world factory floors (Forbes, 2025).
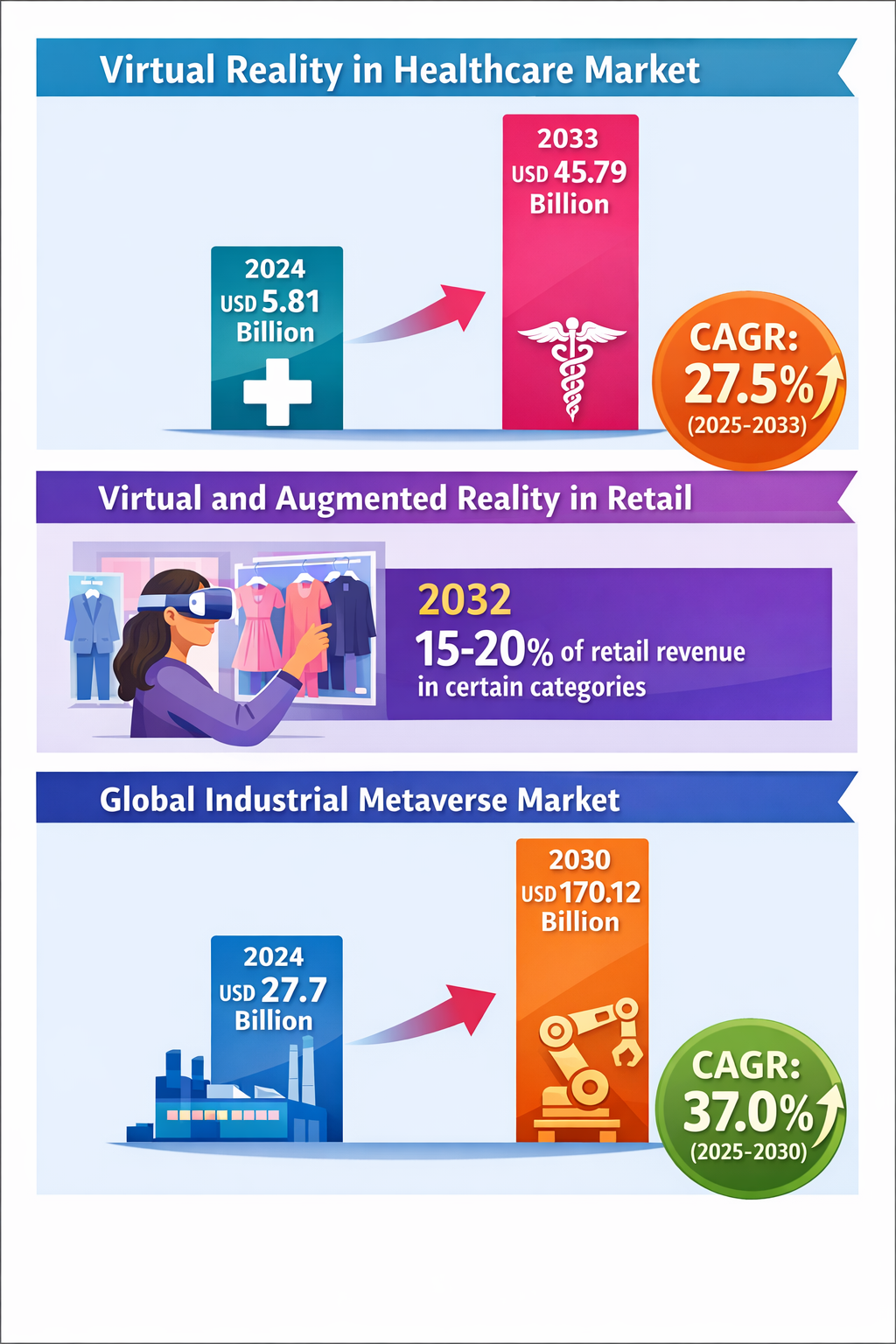
Simultaneously, regulatory bodies are preparing to address this shift. Healthcare, a sector beginning to adopt digital twin technology for clinical care, is developing regulatory frameworks and validation standards to ensure safety and compliance (Trantor Inc., 2025). This move signals a broad institutional acceptance, which may spill over into manufacturing and other industries reliant on rigorous compliance.
The industrial metaverse could add $1.5 trillion to the global economy by 2035 by improving operational efficiencies, reducing downtime, and accelerating innovation cycles (Ian Khan, 2025). In parallel, more firms are expected to allocate dedicated budgets and teams to metaverse initiatives, with 45% of the top 2,000 companies projected to have specialized metaverse units by 2027 (Ian Khan, 2025).
Complementing these industrial shifts, augmented reality experiences are becoming leaner and smarter, focusing less on expansive virtual worlds and more on practical, situational applications such as maintenance guidance, training, and logistics support (Glass Almanac, 2025). This evolution supports more widespread adoption of AR-enabled interfaces as part of the industrial metaverse, especially as hardware becomes lighter and more affordable.
Logistics and supply chain management are also embracing enhanced visibility through digital control towers integrated with AI and digital twins. Investments paused in 2025 are expected to rebound, suggesting that decision-makers recognize the value of these tools to improve responsiveness and reduce disruptions (SCLAA, 2026).
Overall, the industrial metaverse represents a composite trend—where multiple nascent technologies and operational needs converge, creating a new ecosystem that stretches beyond manufacturing to affect adjacent sectors.
Why is this Important?
The industrial metaverse emerges not just as a technological innovation but as a systemic enabler with wide-reaching implications for efficiency, resilience, and competitiveness. For manufacturers, virtual environments combined with AR interfaces could drastically cut downtime by enabling real-time diagnostics, remote expertise, and predictive maintenance. This responsiveness might translate into substantial cost savings and increased asset utilization.
For supply chains, integrated digital twins offer end-to-end visibility uncommon in legacy systems. This could provide early warning of disruptions, better demand forecasting, and more agile responses to logistical shocks. The potential to simulate scenarios and optimize workflows virtually may also improve environmental sustainability by reducing waste and emissions.
In healthcare, adopting industrial metaverse concepts could enhance device manufacturing, personalize treatment delivery, and accelerate clinical trials through precise, virtualized patient and equipment models. Regulation development underway suggests that healthcare’s experience may inform other regulated domains entering this space.
Retail and commerce could also feel the ripple effects as physical and digital boundaries blur. The industrial metaverse’s applications in product design, inventory management, and consumer engagement may create seamless experiences linking manufacturing directly to end-users in new ways.
Governments and policymakers must consider the implications for workforce skills, data security, privacy, and ethical use of virtual operational environments. Preparing regulatory and training frameworks in parallel is crucial to avoid bottlenecks that could stifle adoption.
Implications
The rising industrial metaverse will likely require organizations to rethink technology investments and workforce development priorities. Businesses that start experimenting now with integrated digital twin and AR platforms may gain critical early-mover advantages by fine-tuning workflows and building institutional knowledge.
Collaboration across sectors will become more important. Manufacturers, logistics providers, healthcare entities, and regulators may need to jointly develop interoperability standards and validation protocols. Shared learning can accelerate adoption while controlling risks related to reliability and security.
Investment strategies should anticipate gradual shifts rather than sudden transformations. The integration of digital twins, AI, blockchain, and AR will evolve over the next five to ten years, with waves of innovation triggered as hardware matures and digital infrastructures expand.
Companies should prioritize data governance and cybersecurity. Industrial metaverse environments will generate vast amounts of operational data, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks or accidental exposures. Balancing openness for collaboration and data protection will be crucial.
Radical changes to workforce roles and skills may emerge. Operators and engineers may need training to operate within mixed-reality environments, interpret AI insights, and respond to virtual alerts. Educational entities and corporate training programs could incorporate immersive learning technologies, leveraging the same environments driving industrial transformation.
Finally, the industrial metaverse could influence how companies approach sustainability. Enhanced simulation capabilities might allow for more precise energy optimization and waste reduction, aligning industrial growth with environmental targets.
Questions
- What interoperability standards and regulatory frameworks are needed to ensure safe and efficient industrial metaverse deployment across sectors?
- How can organizations build the internal capabilities to integrate AI, IoT, AR, blockchain, and digital twins into cohesive operational platforms?
- What workforce skills and training programs will prepare employees to operate and innovate within industrial metaverse environments?
- How can data governance models balance the need for collaboration with security and privacy concerns in these integrated virtual-physical systems?
- What early use cases should industries focus on to demonstrate value and reduce barriers to wider adoption?
- How might the industrial metaverse contributions to operational efficiency align with corporate sustainability and social responsibility goals?
- What cross-industry collaborations or public-private partnerships could accelerate innovation and standardization in this space?
Keywords
industrial metaverse; digital twin; augmented reality; artificial intelligence; Internet of Things (IoT); blockchain; supply chain visibility; industrial innovation; workforce skills; regulatory frameworks
Bibliography
- 7 AR Shifts in 2025 That Explain Why Smart Glasses Race Heats Up. Glass Almanac
- 6 Defining Manufacturing Trends of 2026. Forbes
- In 2025, Expect Cutting-Edge Technological Innovations That Enhance the Onboard Experience. Vocal Media
- Promising Virtual Reality Stocks to Watch Today. MarketBeat
- What Awaits the Logistics and Supply Chain Industry in 2026? SCLAA
- Digital Twins in Healthcare: Regulation, Standards and Validation Frameworks. Trantor Inc.
- The Future of the Metaverse: A 10-Year Strategic Outlook and Digital Transformation Forecast. Ian Khan
- The Industrial Metaverse Could Add $1.5 Trillion to the Global Economy by 2035. Ian Khan
- 2025: A Year of Smarter, Greener, Faster Air Cargo. Stat Times